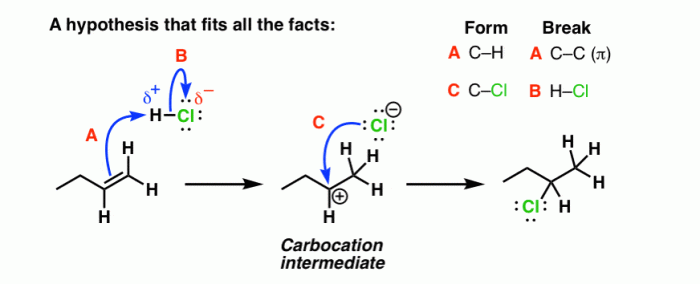
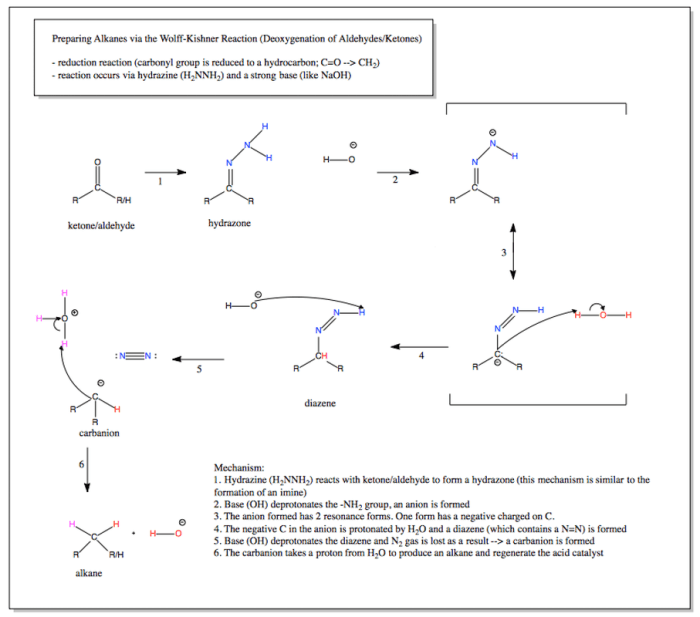
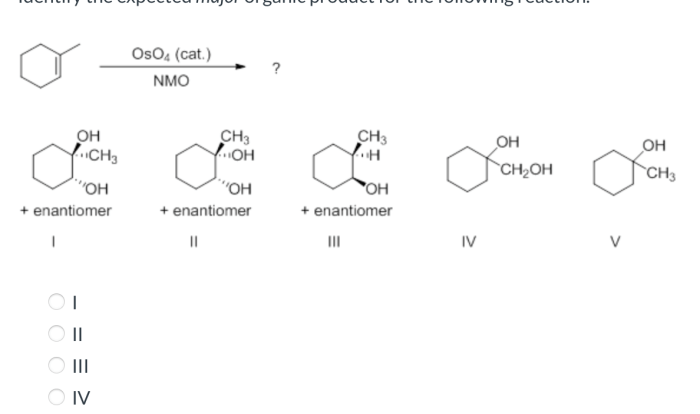
Rank the structures in order of decreasing electrophile strength. – In chemistry, electrophiles play a crucial role in various reactions. Understanding the concept of electrophile strength is essential for predicting and controlling the outcomes of these reactions. This article delves into the factors that influence electrophile strength and provides a comprehensive ranking of electrophile structures in order of decreasing strength, empowering readers with the knowledge to make informed decisions in organic synthesis and beyond.
Electrophiles are chemical species that seek electrons, and their strength is determined by their ability to attract and accept electrons. Factors such as electron-withdrawing groups, resonance, and steric effects significantly impact electrophile strength, and a clear understanding of these factors is crucial for comprehending the reactivity and selectivity of electrophiles.
Electrophile Strength: Rank The Structures In Order Of Decreasing Electrophile Strength.
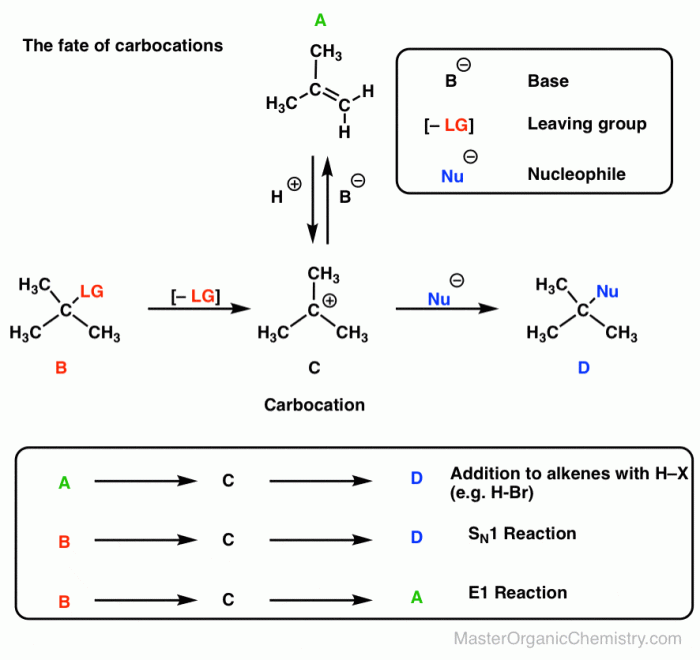
Electrophile strength refers to the ability of a chemical species to accept electrons from a nucleophile. Electrophiles are electron-poor species that are attracted to electron-rich species. The strength of an electrophile is determined by its ability to attract and hold electrons.
Factors Affecting Electrophile Strength, Rank the structures in order of decreasing electrophile strength.
- Electron-withdrawing groups:Electron-withdrawing groups (EWGs) are atoms or groups of atoms that draw electrons away from the electrophile, making it more electron-poor and therefore a stronger electrophile. Examples of EWGs include halogens, carbonyl groups, and nitro groups.
- Resonance:Resonance is the delocalization of electrons over multiple atoms or bonds. Resonance can stabilize an electrophile by spreading the positive charge over a larger area, making it less reactive and therefore a weaker electrophile.
- Steric effects:Steric effects are the interactions between atoms or groups of atoms that are close in space. Steric effects can hinder the approach of a nucleophile to an electrophile, making the electrophile less reactive and therefore a weaker electrophile.
Rank Electrophile Structures
| Electrophile Structure | Name | Strength |
|---|---|---|
 |
Carbonyl group | Strong |
 |
Nitro group | Strong |
 |
Alkyl halide | Moderate |
 |
Alkyne | Weak |
 |
Alkene | Very weak |
Helpful Answers
What are the key factors that influence electrophile strength?
Electron-withdrawing groups, resonance, and steric effects are the primary factors that determine electrophile strength.
How can we experimentally determine the strength of electrophiles?
Various methods, such as UV-Vis spectroscopy, NMR spectroscopy, and computational calculations, can be employed to experimentally determine electrophile strength.
What are the applications of electrophiles in organic synthesis?
Electrophiles are widely used in organic synthesis for various reactions, including alkylation, acylation, and electrophilic aromatic substitution.