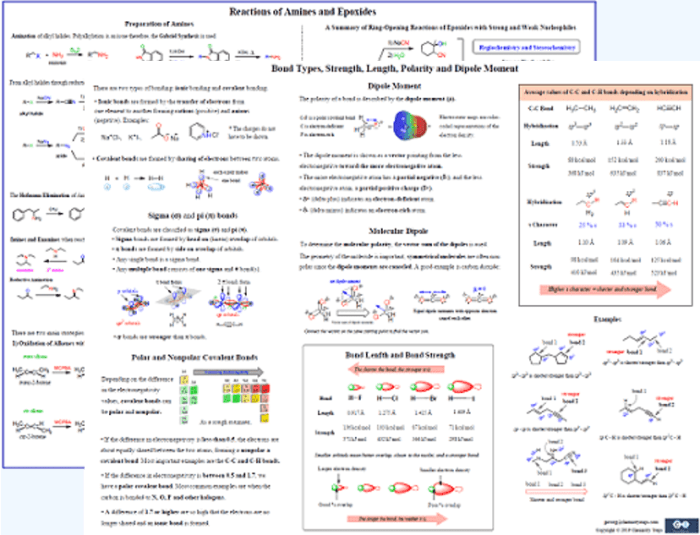
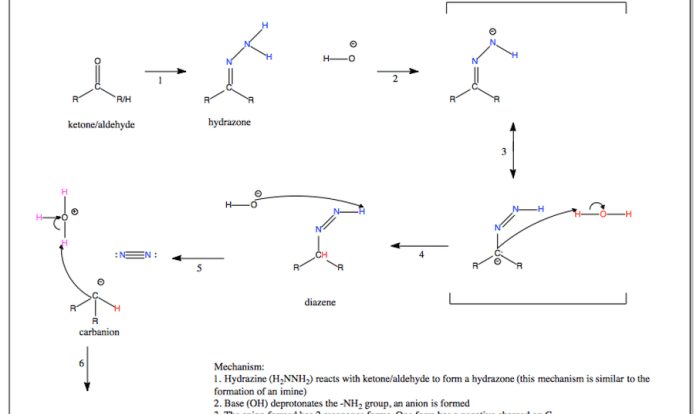
Introducing the organic chemistry nomenclature cheat sheet, an invaluable resource that simplifies the complex world of organic compound naming. This cheat sheet provides a comprehensive overview of IUPAC nomenclature rules, empowering you to navigate the intricacies of organic chemistry with confidence.
Delving into the core principles and key rules, this cheat sheet guides you through the systematic naming of organic compounds, ensuring accuracy and consistency in your chemical communication.
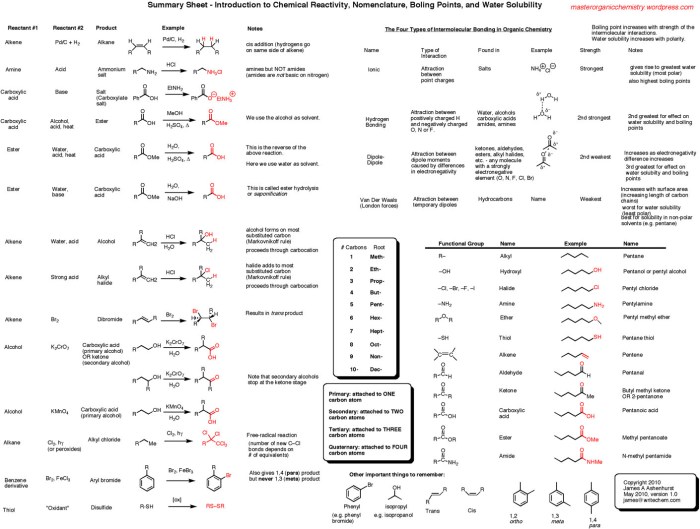
IUPAC Nomenclature Rules: Organic Chemistry Nomenclature Cheat Sheet
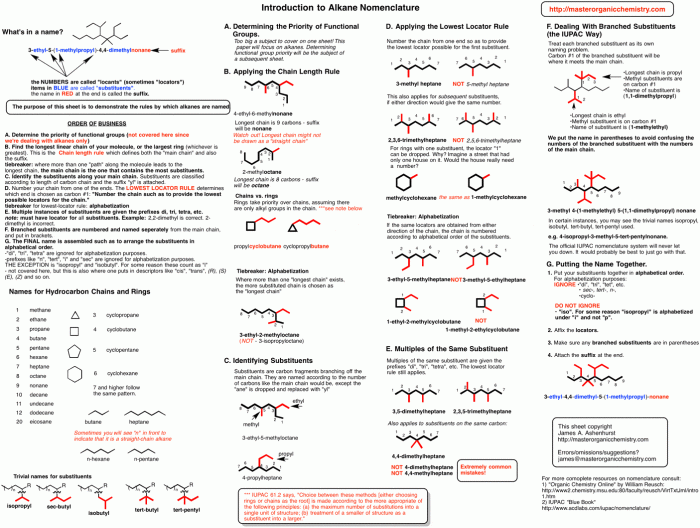
IUPAC nomenclature is a standardized system for naming organic compounds. It is essential for communication and understanding in the field of organic chemistry. The rules were developed by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) to ensure that organic compounds are named consistently and unambiguously.
The key principles of IUPAC nomenclature include:
- The name of an organic compound is based on its structure.
- The parent chain is the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms in the molecule.
- Functional groups are groups of atoms that have specific chemical properties and are named using prefixes and suffixes.
- Substituents are atoms or groups of atoms that are attached to the parent chain.
Functional Groups
Functional groups are groups of atoms that have specific chemical properties. They are named using prefixes and suffixes. The most common functional groups include:
| Functional Group | Prefix | Suffix |
|---|---|---|
| Alkane | alk- | -ane |
| Alkene | alken- | -ene |
| Alkyne | alkyn- | -yne |
| Alcohol | hydroxy- | -ol |
| Ether | alkoxy- | -ether |
| Amine | amino- | -amine |
| Ketone | oxo- | -one |
| Aldehyde | oxo- | -al |
| Carboxylic acid | carboxy- | -oic acid |
Parent Chains
The parent chain is the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms in a molecule. It is used as the basis for naming the compound.
To determine the parent chain, follow these rules:
- Identify the longest chain of carbon atoms in the molecule.
- If there is a tie, choose the chain that contains the most double or triple bonds.
- If there is still a tie, choose the chain that has the highest priority functional group.
Alkyl and Alkenyl Groups
Alkyl groups are groups of atoms that are derived from alkanes. Alkenyl groups are groups of atoms that are derived from alkenes.
The prefixes used to indicate the number of carbon atoms in alkyl and alkenyl groups are:
| Number of Carbon Atoms | Prefix |
|---|---|
| 1 | meth- |
| 2 | eth- |
| 3 | prop- |
| 4 | but- |
| 5 | pent- |
| 6 | hex- |
Cyclic Compounds
Cyclic compounds are compounds that contain one or more rings of carbon atoms.
The prefixes used to indicate the number of carbon atoms in cyclic compounds are:
| Number of Carbon Atoms | Prefix |
|---|---|
| 3 | cycloprop- |
| 4 | cyclobut- |
| 5 | cyclopent- |
| 6 | cyclohex- |
Substitution and Branching, Organic chemistry nomenclature cheat sheet
Substitution and branching are common features of organic compounds.
To name a compound with substituents and branches, follow these rules:
- Identify the parent chain.
- Identify the substituents and branches.
- Assign locants to the substituents and branches.
- Name the compound using the prefixes and suffixes for the functional groups, substituents, and branches.
Essential Questionnaire
What is the purpose of IUPAC nomenclature in organic chemistry?
IUPAC nomenclature provides a standardized system for naming organic compounds, ensuring consistency and clarity in chemical communication.
How do I identify the parent chain in an organic compound?
The parent chain is the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms in the molecule. It determines the base name of the compound.
What is the difference between alkyl and alkenyl groups?
Alkyl groups contain only single bonds between carbon atoms, while alkenyl groups contain at least one double bond between carbon atoms.