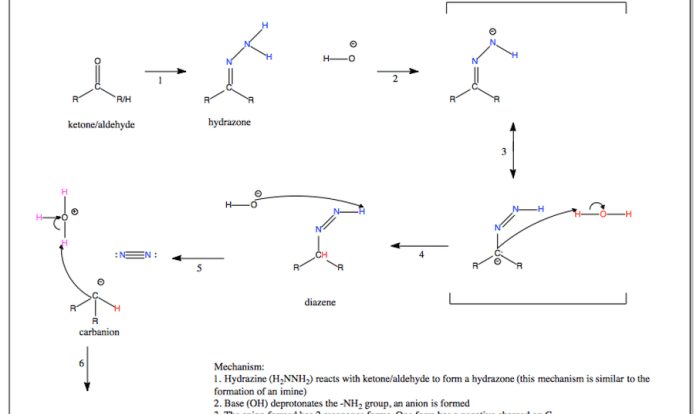
Draw the expected major product of the following reaction. – Delving into the realm of organic chemistry, we embark on a journey to unravel the intricacies of predicting the expected major product of a given reaction. This concept lies at the heart of successful organic synthesis, guiding chemists in their quest to construct complex molecules with precision and efficiency.
The formation of a major product is influenced by a delicate interplay of factors, including the inherent reactivity of the reactants, the reaction mechanism, and the influence of regio- and stereoselectivity. Understanding these factors empowers chemists to anticipate the outcome of reactions and design synthetic strategies accordingly.
Expected Major Product
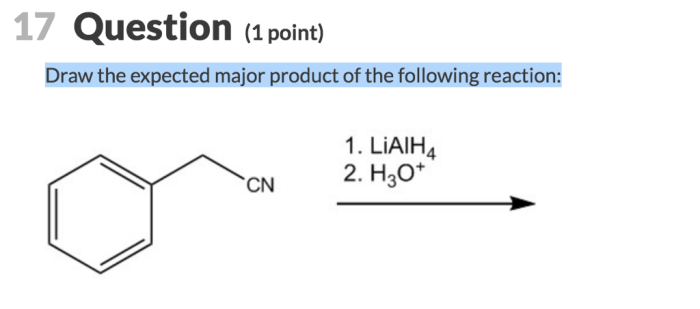
In organic chemistry, the expected major product is the most likely product of a reaction based on its mechanism and the reactivity of the reactants. The formation of the major product is influenced by factors such as:
- Stability: The more stable the product, the more likely it is to form.
- Kinetics: The faster the reaction pathway leading to a product, the more likely that product is to form.
- Thermodynamics: The reaction with the lowest activation energy is more likely to occur, leading to the formation of the major product.
The concepts of regioselectivity and stereoselectivity are closely related to the expected major product. Regioselectivity refers to the preference for a reaction to occur at a particular atom or group of atoms, while stereoselectivity refers to the preference for a reaction to produce a specific stereoisomer.
Reaction Mechanisms: Draw The Expected Major Product Of The Following Reaction.
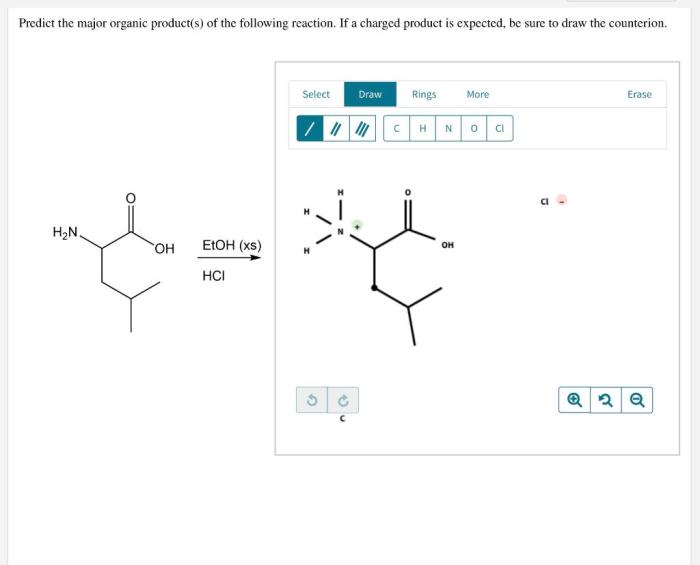
The type of reaction mechanism can significantly influence the expected major product. Common reaction mechanisms include:
- Nucleophilic substitution: A nucleophile attacks an electrophile, leading to the replacement of a leaving group.
- Electrophilic addition: An electrophile adds to a double or triple bond, forming a new bond.
- Radical reactions: Reactions involving the formation and reaction of free radicals.
- Pericyclic reactions: Reactions that involve the concerted movement of electrons in a cyclic transition state.
The choice of reaction mechanism is often dictated by the nature of the reactants and the reaction conditions, such as temperature, solvent, and catalysts.
Regioselectivity and Stereoselectivity
Regioselectivityrefers to the preference for a reaction to occur at a particular atom or group of atoms. Factors influencing regioselectivity include:
- Steric hindrance: Bulky groups can block access to certain reaction sites.
- Electronic effects: Electron-withdrawing groups can direct reactions to more electron-rich sites.
Stereoselectivityrefers to the preference for a reaction to produce a specific stereoisomer. Factors influencing stereoselectivity include:
- Chiral reagents or catalysts: These can induce chirality in the product.
- Conformational effects: The conformation of the reactants can influence the stereochemical outcome of a reaction.
Applications in Organic Synthesis
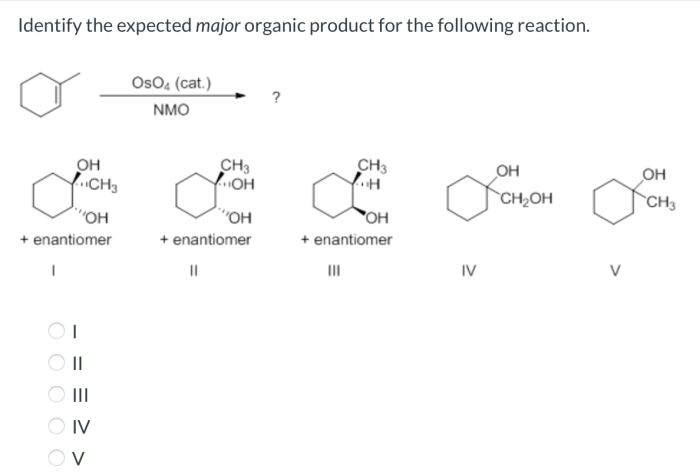
The concept of the expected major product is crucial in organic synthesis, as it allows chemists to predict the products of reactions and design synthetic strategies. By understanding the factors that influence the formation of the major product, chemists can optimize reaction conditions to achieve the desired outcome.
For example, in the synthesis of a target molecule, the expected major product can be used to identify the starting materials and reaction pathway that will most efficiently lead to the desired product. This knowledge helps chemists avoid unnecessary steps and optimize the efficiency of their synthetic processes.
FAQ Summary
What is the definition of the expected major product in organic chemistry?
The expected major product is the product that is formed in the greatest quantity under a given set of reaction conditions.
What factors influence the formation of the major product?
The formation of the major product is influenced by the inherent reactivity of the reactants, the reaction mechanism, and the influence of regio- and stereoselectivity.
What is the difference between regioselectivity and stereoselectivity?
Regioselectivity refers to the preference for one regioisomer over another, while stereoselectivity refers to the preference for one stereoisomer over another.